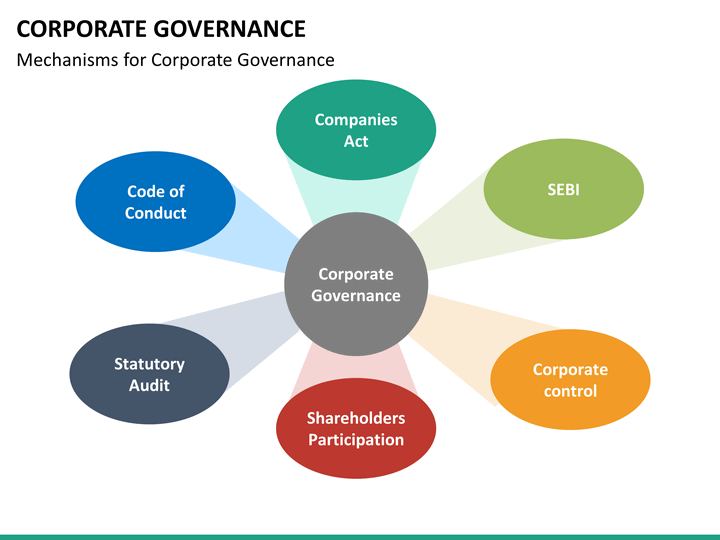
Corporate governance in India is governed by the Companies Act 2013, which mandates that companies have a board of directors and outlines their duties, including acting within the company’s constitution and avoiding conflicts of interest. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) enforces Clause 49, requiring listed companies to have a certain proportion of independent directors and maintain internal controls.
Additionally, the Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA) supports the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in developing corporate laws and provides training to enhance governance standards.
Corporate governance has to be effectively done using Committees as prescribe by law .
Under the Companies Act, 2013:
- Audit Committee: Ensures the integrity of financial reporting and compliance with legal requirements.
- Nomination and Remuneration Committee: Oversees the selection and remuneration of directors and key managerial personnel.
- Stakeholder Relationship Committee: Addresses the grievances of shareholders and other stakeholders.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Committee: Formulates and monitors the CSR policy of the company.
Under SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015:
- Audit Committee: Similar to the one under the Companies Act, it ensures financial integrity and compliance.
- Nomination and Remuneration Committee: Manages the nomination and remuneration of directors and key personnel.
- Stakeholder Relationship Committee: Handles stakeholder grievances and issues
Even other companies that has not comply with such compliances issues if still put in practice of then the same is bound to perform well ahead of contemporaries and thus provide sustainable work environment to not alone to its employees but also to its clients , supply chain and investors .
Under the Companies Act, 2013, the Audit Committee plays a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of a company’s financial reporting and compliance with legal requirements. Here are some key functions of the Audit Committee:
- Financial Reporting: Oversee the financial reporting process and ensure the integrity of the company’s financial statements.
- Internal Controls: Monitor and evaluate the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal control systems.
- Auditors: Recommend the appointment, reappointment, and removal of auditors, and approve their remuneration.
- Audit Plans: Review and approve the scope of internal and statutory audit plans.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with accounting standards, stock exchange, and legal requirements related to financial statements.
- Risk Management: Assess financial risks and implement mitigation strategies.
- Fraud Detection: Review mechanisms for detecting fraud and oversee investigations into financial irregularities.
- Whistleblower Mechanism: Establish and monitor a robust whistleblower mechanism for reporting fraudulent activities.
These functions help enhance corporate governance and ensure the company’s financial health and transparency. Anything specific you would like to delve into about the Audit Committee’s role?
Under the SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015, the Audit Committee has several important functions aimed at ensuring effective corporate governance and financial integrity. Here’s a summary of its key functions:
- Financial Reporting: Monitor and review the integrity of the company’s financial statements and any formal announcements relating to financial performance.
- Internal Controls: Assess and ensure the adequacy and effectiveness of the company’s internal control systems and risk management policies.
- Internal Audit: Review the scope of the internal audit function, including the independence, authority, and performance of the internal auditors.
- Statutory Audit: Recommend the appointment, reappointment, or removal of statutory auditors, and approve their remuneration. Review and monitor the auditor’s independence and performance.
- Whistleblower Mechanism: Establish and oversee a robust whistleblower mechanism to encourage and protect employees who report fraudulent activities or other concerns.
- Related Party Transactions: Review and approve all related party transactions to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and safeguard the interests of stakeholders.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements related to financial reporting and disclosures.